Understanding Acanthosis Nigricans: Causes, Risk Factors, and Treatment Options
Acanthosis Nigricans is a common skin condition characterized by areas of dark, thick, velvety discoloration. While it can affect anyone worldwide, understanding its causes and treatment options is essential for managing both the cosmetic and health-related aspects of this condition. This comprehensive guide explores what Acanthosis Nigricans is, who is at risk, and the various approaches available for treatment and management.
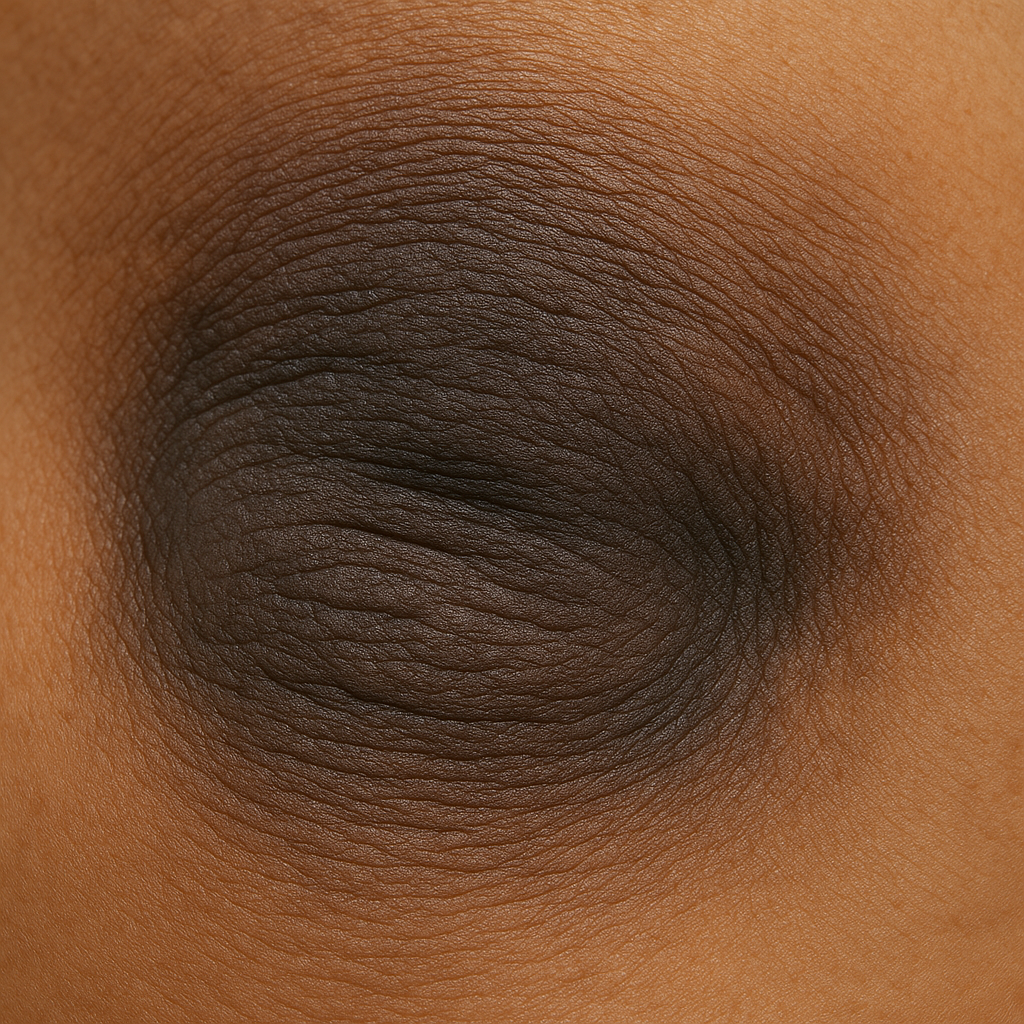
What is Acanthosis Nigricans?
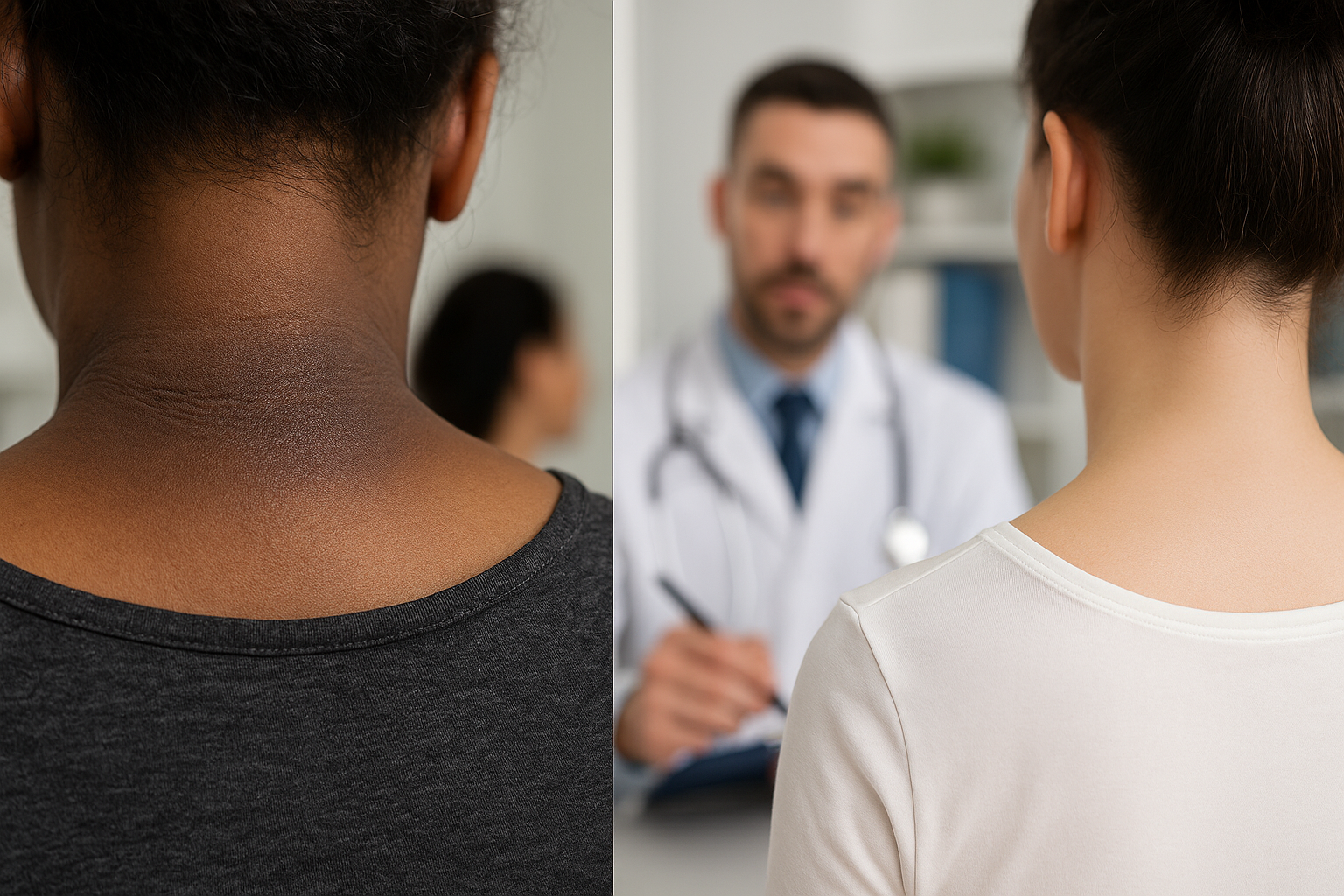
Acanthosis Nigricans is a pigmentation disorder that manifests as darkened patches of skin with a distinctive thick and velvety texture. Unlike temporary skin discoloration, this condition results from changes at the cellular level within the skin itself. The affected areas typically appear darker than the surrounding skin and may feel slightly raised or thickened to the touch.
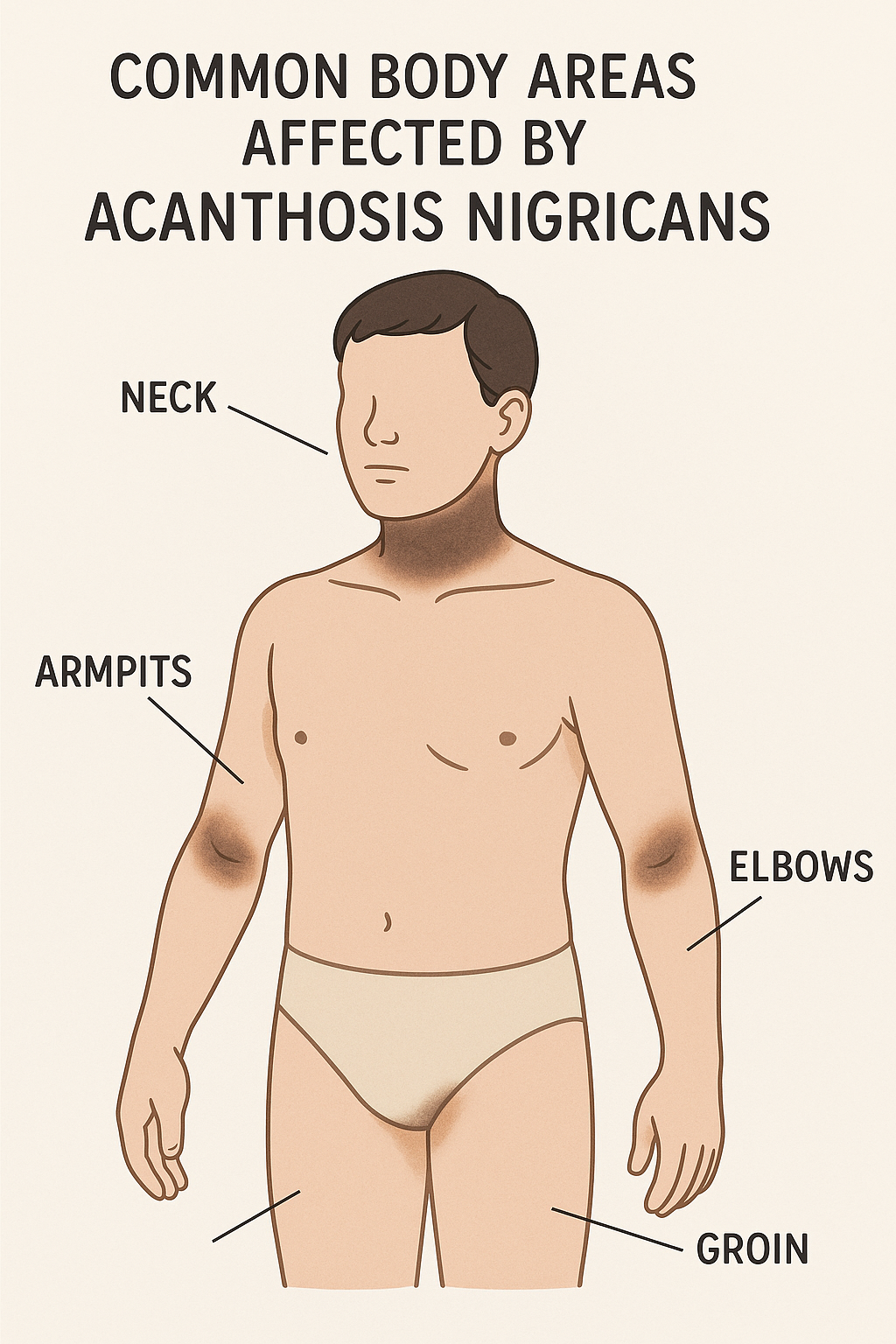
These characteristic dark patches commonly develop in body areas where skin naturally folds or creases, including:
- Armpits (axillae)
- Groin and inner thighs
- Neck, particularly the back and sides
- Elbows and knees
- Knuckles and finger joints
- Lips and mouth area
- Palms of the hands
- Soles of the feet
The condition affects individuals of all ages, genders, and backgrounds, though certain populations experience higher prevalence rates. Studies indicate that between 7% and 74% of people may experience some degree of Acanthosis Nigricans during their lifetime, with significant variation based on factors such as age, genetic background, and overall health status.
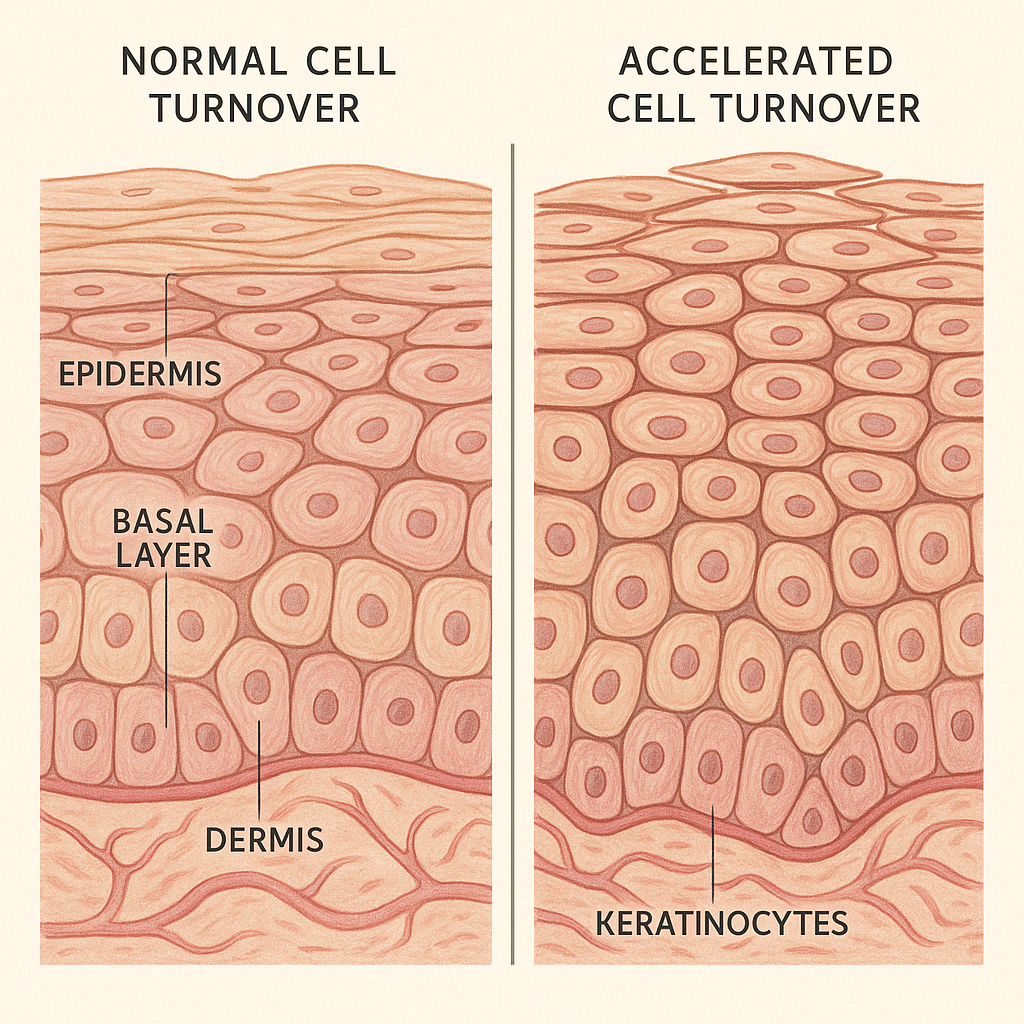
Understanding the Causes of Acanthosis Nigricans
The darkening and thickening of skin associated with Acanthosis Nigricans occurs when epidermal skin cells begin to reproduce at an abnormally rapid rate. This accelerated cell growth leads to the accumulation of pigmented cells in localized areas, creating the characteristic dark, velvety patches.
The most common trigger for this abnormal cell growth is elevated insulin levels in the bloodstream. When insulin levels remain consistently high, they can stimulate excessive growth of skin cells and increase melanin production. However, in less common cases, the condition may result from certain medications, underlying medical conditions, or rarely, internal cancers.
While the discoloration itself is generally not harmful, many people seek treatment for cosmetic reasons or because the condition indicates an underlying health concern that requires attention. It’s important to understand that Acanthosis Nigricans often serves as a visible marker of internal metabolic changes, making professional medical evaluation valuable for anyone experiencing these symptoms.
Who Is at Risk for Developing Acanthosis Nigricans?
Acanthosis Nigricans can affect both men and women equally, though certain factors significantly increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Understanding these risk factors helps individuals identify potential concerns early and seek appropriate medical guidance.
Primary Risk Factors
Excess Body Weight: Individuals carrying extra weight face substantially higher risk. Research indicates that more than half of adults whose weight exceeds 200% of their ideal body weight will develop some degree of Acanthosis Nigricans. The condition often improves significantly with weight loss, suggesting a strong connection between body weight and skin changes.
Insulin Resistance and Diabetes: Perhaps the most significant risk factor, insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin’s effects. This condition frequently precedes type 2 diabetes and strongly correlates with Acanthosis Nigricans development. People with diagnosed diabetes or pre-diabetic conditions should be particularly aware of this connection.
Hormonal Imbalances: Various endocrine disorders increase susceptibility to skin darkening. Conditions such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), and other hormone-related disorders can trigger or exacerbate Acanthosis Nigricans. These conditions affect how the body processes insulin and regulates cell growth.
Genetic Factors: Family history plays an important role in determining risk. Acanthosis Nigricans appears to run in families, suggesting inherited genetic factors that influence skin cell behavior and insulin sensitivity. If close family members have experienced this condition, individual risk increases.
Ethnic and Genetic Background: Prevalence varies significantly among different populations worldwide. Studies show that people of Indigenous American descent experience the highest rates, followed by those of African, Hispanic, and European ancestry. However, the condition can affect individuals from any background.
Age Considerations: While Acanthosis Nigricans can appear at any age, it often becomes noticeable during adolescence when hormonal changes are most pronounced. However, adults experiencing metabolic changes or weight gain may also develop the condition later in life.

Secondary Causes and Contributing Factors
Medications: Certain prescription medications can trigger or worsen Acanthosis Nigricans. Common culprits include high-dose niacin (vitamin B3), hormonal contraceptives, corticosteroids, and some medications used to treat other conditions. If you develop skin darkening after starting a new medication, consult with your healthcare provider about possible alternatives.
Frequent Hair Removal: Repeated shaving, waxing, or plucking can contribute to skin darkening in affected areas. The mechanical irritation and inflammation from regular hair removal may stimulate excessive pigment cell production, particularly in sensitive areas like the armpits and groin.
Rare Cancer Association: In uncommon cases, Acanthosis Nigricans may signal the presence of internal cancers, particularly tumors of the stomach, liver, or other organs. This malignant form typically appears suddenly, progresses rapidly, and may be more extensive than the benign forms. Any sudden onset of widespread skin darkening warrants immediate medical evaluation.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Healthcare professionals can typically diagnose Acanthosis Nigricans through visual examination of the affected skin. The characteristic appearance of dark, velvety patches in typical locations makes the condition relatively straightforward to identify. However, accurate diagnosis requires more than just recognizing the skin changes—it involves investigating the underlying causes.
Comprehensive Medical Assessment
A thorough medical evaluation typically includes:
Blood Glucose Testing: Measuring blood sugar levels helps identify diabetes or pre-diabetic conditions. Your healthcare provider may order fasting blood glucose tests or hemoglobin A1C tests to assess long-term glucose control.
Insulin Level Assessment: Testing insulin levels, particularly fasting insulin, helps determine whether insulin resistance is contributing to the skin changes. Elevated insulin levels often appear before blood sugar becomes abnormal.
Medication Review: A complete review of all medications, supplements, vitamins, and dietary aids is essential. Be sure to inform your healthcare provider about any over-the-counter products, herbal supplements, or bodybuilding supplements you use, as these can sometimes contribute to the condition.
Hormone Evaluation: Testing thyroid function and other hormones may be necessary, particularly if other symptoms suggest endocrine disorders.
Skin Biopsy: In rare cases where the diagnosis is uncertain or when cancer is suspected, a small skin biopsy may be performed. This involves removing a tiny sample of affected skin for microscopic examination.
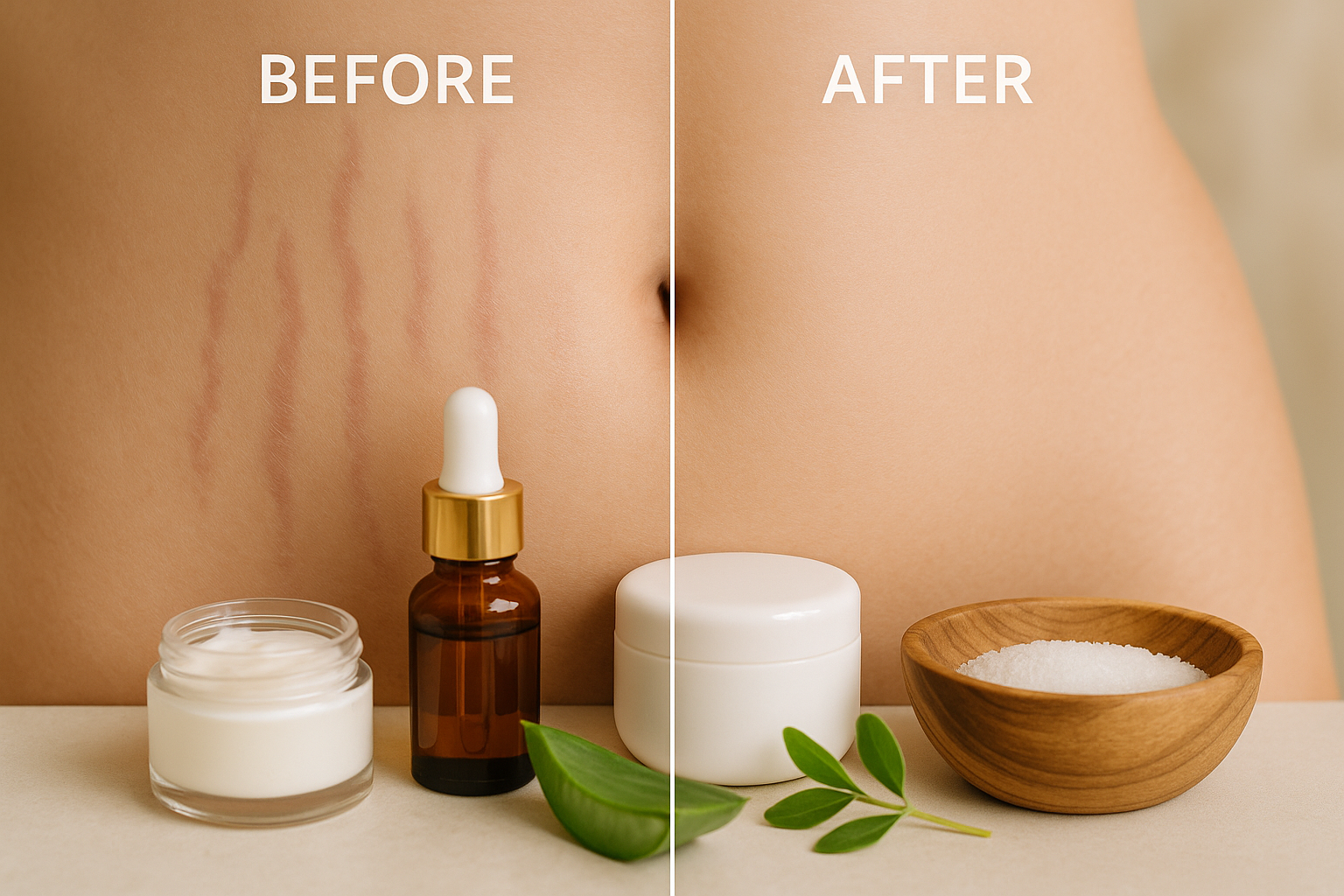
Treatment Approaches and Management Strategies
Effective treatment of Acanthosis Nigricans focuses on two primary goals: addressing the underlying cause and improving the skin’s appearance. The most successful outcomes typically result from a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatment of root causes with targeted skin care strategies.
Addressing Underlying Causes
The most effective long-term strategy involves treating the condition’s root causes:
Weight Management: For individuals who are overweight, gradual weight loss through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity often leads to significant improvement in skin appearance. As weight decreases and insulin sensitivity improves, darkened areas may lighten naturally over time.
Diabetes Management: If insulin resistance or diabetes is present, working with healthcare providers to optimize blood sugar control is essential. This may involve dietary modifications, exercise programs, and possibly medication to improve insulin sensitivity.
Medication Adjustment: If a particular medication is contributing to the condition, your healthcare provider may be able to suggest alternative treatments that don’t have this side effect.
Hormone Treatment: Addressing underlying hormonal imbalances through appropriate medical treatment can help resolve associated skin changes.

Topical Treatments and Prescription Options
Various topical treatments can help improve the appearance of darkened skin. These should always be used under professional medical guidance:
Retinoid Creams: These vitamin A derivatives promote skin cell turnover and exfoliation, helping to remove darkened outer layers and encourage healthier skin growth. They can gradually improve skin texture and reduce discoloration over time with consistent use.
Hydroquinone Preparations: This skin-lightening agent works by reducing melanin production in treated areas. It requires careful use and medical supervision to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Chemical Exfoliants: Professional-grade chemical peels containing trichloroacetic acid (TCA) or other exfoliating agents can remove damaged skin layers and promote regeneration of healthier skin.
Vitamin D-Based Creams: Calcipotriene and similar compounds can help reduce excessive pigmentation in some individuals by modulating skin cell growth and melanin production.
Antibacterial Treatments: Topical antibiotics or antibacterial cleansers may help in cases where bacterial colonization of hair follicles contributes to darkening. Reducing bacterial populations in affected areas can sometimes lead to lightening of the skin.

Advanced Professional Treatments
Laser Therapy: Various laser treatments can target excessive pigmentation and promote skin renewal. Laser therapy may also provide long-term hair removal in affected areas, which can reduce irritation from shaving and help prevent further darkening. This approach requires multiple sessions and should only be performed by qualified professionals.
Dermabrasion and Microdermabrasion: These mechanical exfoliation techniques remove outer skin layers, potentially improving appearance over time with repeated treatments.
Skin Care and Prevention Strategies
Proper daily skin care can help prevent worsening of the condition and support other treatments:
Gentle Hair Removal Practices: If you remove hair from affected areas, use gentle techniques to minimize skin irritation. Always use quality shaving products designed for sensitive skin, and consider alternatives to frequent shaving such as professional laser hair removal or electric trimmers that don’t irritate the skin surface.
Moisturization: Regular use of fragrance-free, gentle moisturizers helps maintain skin health and reduce irritation. Apply moisturizer immediately after bathing and after any hair removal to soothe the skin.
Mild Cleansing: Use gentle, non-irritating soaps or cleansers formulated for sensitive skin. Avoid harsh scrubbing or abrasive products that can cause further irritation.
Sun Protection: While sun exposure doesn’t cause Acanthosis Nigricans, protecting treated areas from sun damage is important, especially when using certain topical treatments that increase sun sensitivity.

Natural Remedies and Alternative Approaches
Some individuals explore natural remedies for managing Acanthosis Nigricans, though it’s important to note that scientific evidence supporting these approaches remains limited. If you choose to try natural remedies, discuss them with a healthcare provider first and be aware of potential side effects.
Turmeric (Curcumin): The active compound in turmeric has anti-inflammatory properties and may help with various skin conditions. Some people apply turmeric-based preparations to darkened areas, though research specifically on Acanthosis Nigricans is limited.
Aloe Vera: Known for soothing properties, aloe vera gel may help reduce skin irritation and support overall skin health, though its effects on pigmentation are not well established.
Apple Cider Vinegar: Some advocates suggest diluted apple cider vinegar may help exfoliate skin, though this can cause irritation in sensitive individuals.
Caution with Citrus-Based Remedies: While lemon juice is sometimes suggested for skin lightening, it can cause significant irritation, dryness, and increased sun sensitivity. It may also trigger allergic reactions or worsen conditions like eczema in susceptible individuals. The acidic nature of lemon juice can damage the skin’s protective barrier, potentially causing more harm than benefit.
Sea Cucumber Extract and Other Marine Compounds: Some research suggests certain marine-derived compounds may have skin-benefiting properties, though more studies are needed to confirm effectiveness for Acanthosis Nigricans specifically.
Living with Acanthosis Nigricans: Practical Guidance
While Acanthosis Nigricans can be concerning, especially when first noticed, understanding that it’s manageable and often improvable makes a significant difference. The condition itself is not dangerous, though it may signal underlying health issues that deserve attention.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Consult a healthcare provider if you notice:
- New areas of dark, thickened skin appearing on your body
- Rapid spread or darkening of existing affected areas
- Skin changes accompanied by other symptoms like unexplained weight loss, fatigue, or digestive problems
- Affected areas that become painful, itchy, or develop an unusual odor
- Concerns about diabetes risk or family history of metabolic conditions
Long-Term Management and Expectations
Managing Acanthosis Nigricans often requires patience and a comprehensive approach. Skin improvements typically occur gradually over months rather than weeks. The most successful outcomes generally result from:
- Addressing underlying metabolic conditions like insulin resistance or diabetes
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy body weight through sustainable lifestyle changes
- Following a consistent skin care routine tailored to your specific needs
- Using appropriate medical treatments under professional supervision
- Regular follow-up with healthcare providers to monitor progress and adjust treatments as needed
Remember that while cosmetic concerns are valid, the real importance of recognizing and treating Acanthosis Nigricans lies in what it may reveal about your overall health. Many people who address the underlying causes not only see improvements in their skin but also experience better overall health, increased energy, and reduced risk of serious conditions like type 2 diabetes.

Conclusion: A Treatable Condition with Multiple Solutions
Acanthosis Nigricans, while sometimes distressing due to its visible nature, is a manageable condition with various treatment options available. Whether your primary concern is cosmetic appearance or addressing underlying health issues, working with qualified healthcare providers offers the best path forward.
The key to successful management lies in understanding that this condition often reflects internal metabolic changes. By addressing these root causes while also treating the visible skin changes, most people can achieve significant improvements. Modern medical treatments, proper skin care, and lifestyle modifications all play important roles in managing this condition effectively.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of Acanthosis Nigricans, don’t hesitate to seek professional medical guidance. Early intervention not only helps improve skin appearance but may also prevent or better manage more serious health conditions associated with insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction.


