Understanding Skin Tanning and Essential Aftercare Practices
Achieving a sun-kissed glow has become a popular beauty goal worldwide, with numerous tanning methods available to suit different preferences and lifestyles. However, tanning—whether through natural sun exposure, indoor tanning devices, or spray applications—requires proper aftercare to maintain skin health and prolong results. Without adequate post-tanning care, you may experience dryness, premature aging, uneven tone, or more serious skin concerns. This comprehensive guide explores what happens during the tanning process and provides detailed aftercare strategies to help you maintain healthy, radiant skin while minimizing potential damage.

What Happens During the Tanning Process?
The desire for tanned skin has evolved significantly over the past century. Historically, darker skin was associated with outdoor labor, while pale skin signified wealth and leisure. This perception shifted dramatically in the early 20th century when international travel became more accessible to affluent individuals. Vacationing in sunny destinations during colder months became a status symbol, and returning home with tanned skin demonstrated one’s ability to travel and enjoy leisure time in warm climates.
The cultural shift toward embracing tanned skin gained significant momentum in the 1920s, when fashion icon Coco Chanel popularized the look after returning from a Mediterranean vacation with sun-kissed skin. This marked a turning point in beauty standards, transforming tanned skin from a mark of labor to a symbol of health, vitality, and social status. Winter sports enthusiasts in mountainous regions also contributed to this trend, as the combination of sun reflection off snow and high-altitude exposure created a distinctive healthy glow.
Today, achieving a tan has become more accessible through various methods including natural sunbathing, indoor tanning beds, spray tanning, and self-tanning products. Understanding the biological process behind tanning helps explain why proper aftercare is essential for maintaining skin health.
The Science Behind Skin Tanning
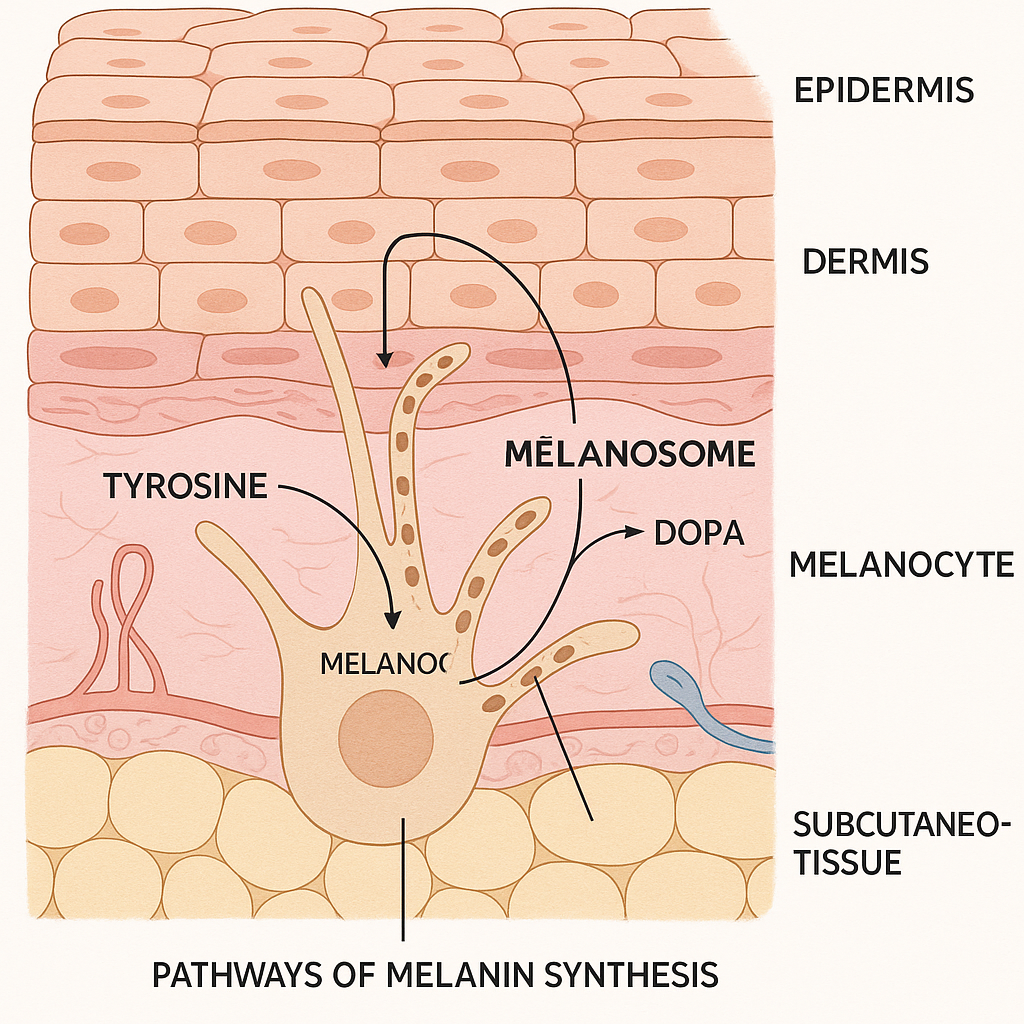
When skin is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation—whether from the sun or artificial sources—it triggers a complex biological defense mechanism. UV rays penetrate the outer layers of skin, prompting specialized cells called melanocytes to produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. This increased melanin production is actually your body’s protective response to prevent deeper tissue damage from UV radiation.
Melanocytes work in conjunction with keratinocytes, which form approximately 90% of the skin’s outermost layer (epidermis). Keratinocytes act as the skin’s first line of defense against environmental threats including microorganisms, heat, chemical exposure, and UV radiation. During tanning, melanin is distributed to keratinocytes, creating a darker pigmentation that absorbs and scatters UV rays before they can cause cellular damage to deeper skin layers.
While this protective mechanism results in the desired bronzed appearance, the process itself creates stress on the skin. UV exposure depletes moisture, generates free radicals, breaks down collagen and elastin fibers, and can cause inflammation. This is why comprehensive aftercare is not merely optional—it’s essential for maintaining skin health and appearance.
Essential Aftercare Practices Following Tanning
Proper post-tanning care can make the difference between healthy, glowing skin and damaged, prematurely aged skin. Whether you’ve spent time in natural sunlight, used an indoor tanning device, or applied self-tanning products, implementing these evidence-based aftercare strategies will help protect your skin, maintain your tan longer, and minimize potential damage.
1. Prioritize Hydration from Within
All forms of tanning—particularly those involving UV exposure—cause significant water loss from skin cells and the body overall. UV radiation increases transepidermal water loss (TEWL), the process by which water passes from the dermis through the epidermis and evaporates from the skin surface. This dehydration affects not only the appearance of your tan but also your skin’s overall health and function.
Increasing your water intake before, during, and after tanning sessions helps counteract this moisture loss. Proper hydration supports cellular function, helps maintain skin elasticity, promotes healing, and can even extend the life of your tan by keeping skin cells plump and healthy. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, increasing this amount on days when you tan or spend extended time outdoors.
In addition to water, consider hydrating beverages rich in electrolytes, which help your body retain moisture more effectively. Coconut water, herbal teas, and water infused with fresh fruits can make hydration more enjoyable while providing additional nutrients that support skin health.

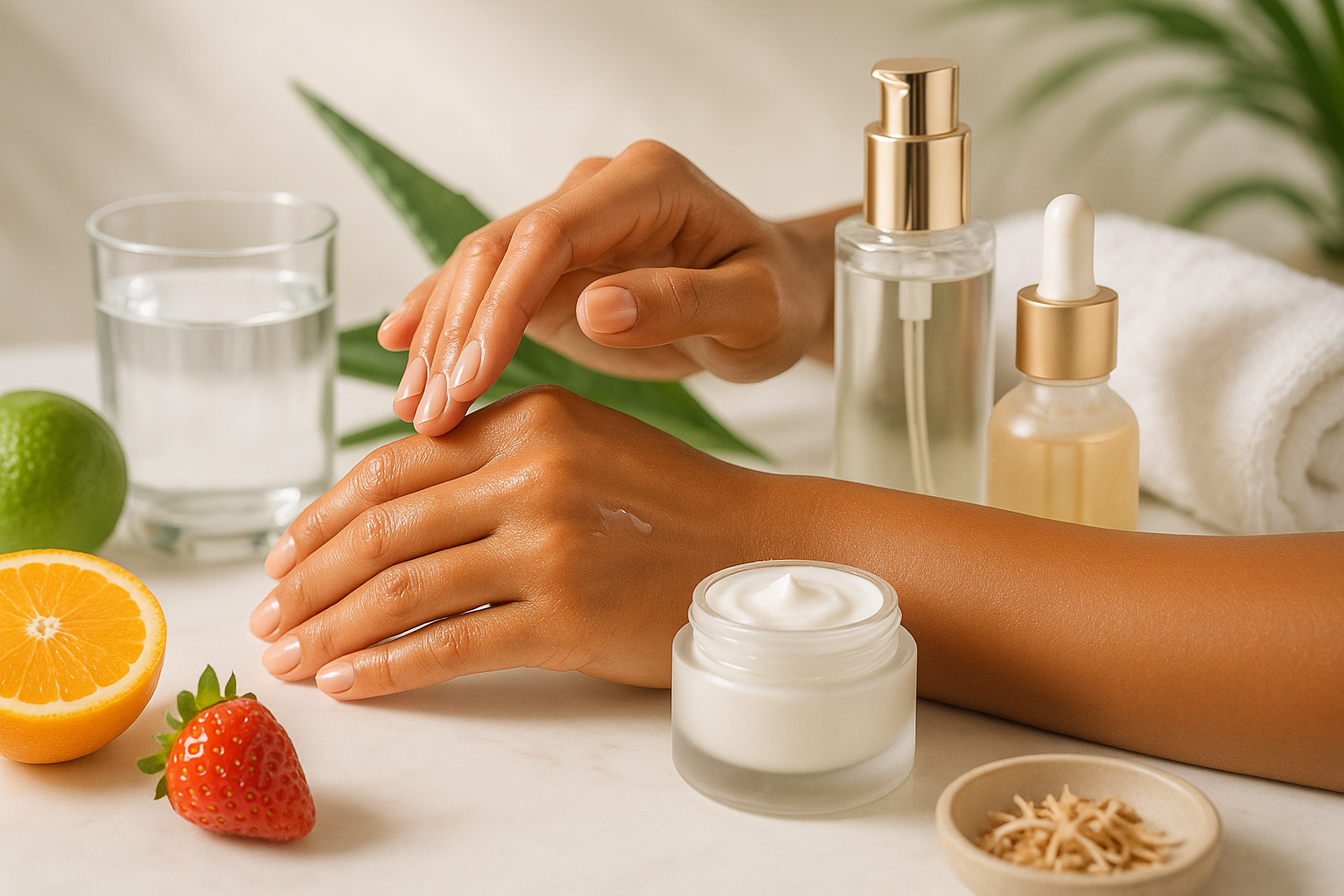
2. Apply Moisturizers and Hydrating Products
While internal hydration is crucial, topical moisture replacement is equally important for post-tanning skincare. After tanning, your skin’s natural moisture barrier is compromised, making it less effective at retaining water and more vulnerable to environmental stressors. Applying quality moisturizing products helps restore this barrier, soothe inflammation, and prevent the dry, flaky appearance that can develop after UV exposure.
Look for moisturizers containing ingredients specifically beneficial for post-tanning care. Hyaluronic acid is particularly effective as it can hold up to 1,000 times its weight in water, drawing moisture into the skin and keeping it hydrated throughout the day. Ceramides help rebuild the skin’s protective barrier, while ingredients like glycerin, aloe vera, and vitamin E provide soothing, anti-inflammatory benefits.
For best results, apply moisturizer to slightly damp skin immediately after showering or bathing, as this helps lock in moisture. Choose fragrance-free formulations if your skin feels sensitive after tanning, and consider using a heavier cream or body butter at night when skin undergoes its natural repair processes.
Specialized after-sun products are designed specifically for post-UV care, often containing cooling ingredients like aloe vera, cucumber extract, or menthol that provide immediate comfort while delivering intensive hydration. These products can be particularly beneficial immediately after sun exposure or tanning sessions.

3. Incorporate Gentle Exfoliation
Exfoliation is the process of removing dead skin cells from the surface layer of your skin. While your body naturally sheds approximately 30,000-40,000 dead skin cells every minute, this process can become uneven after tanning, leading to a patchy appearance as your tan fades. Strategic exfoliation helps maintain an even skin tone, prevents flakiness, and can actually help your tan last longer by removing the outermost damaged cells while preserving the tanned layers beneath.
However, timing and technique are crucial when exfoliating after tanning. Wait at least 48 hours after UV exposure before exfoliating, as your skin needs time to recover and stabilize the newly produced melanin. When you do exfoliate, choose gentle methods rather than harsh scrubs that could irritate already-stressed skin.
Chemical exfoliants containing alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs) in low concentrations can provide gentle exfoliation without mechanical abrasion. Physical exfoliants like soft washcloths, gentle scrubs with fine particles, or exfoliating gloves can also be effective when used with a light touch. Exfoliate no more than 2-3 times per week to avoid over-stressing your skin.
Always follow exfoliation with moisturizer to replenish the skin’s protective barrier and prevent moisture loss from the newly exposed skin cells.

4. Consume Dark Chocolate for Antioxidant Support
Your post-tanning skincare routine shouldn’t focus solely on topical treatments—what you consume also significantly impacts your skin’s ability to recover and maintain health after UV exposure. Dark chocolate, particularly varieties containing 70% cacao or higher, offers surprising benefits for post-tanning skin recovery.
Dark chocolate is rich in flavonoids, powerful plant compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Research has shown that the flavonoids in cacao can improve skin hydration, increase blood flow to the skin, and provide protection against UV-induced damage. These compounds work by neutralizing free radicals—unstable molecules generated by UV exposure that can damage cellular structures, break down collagen, and accelerate skin aging.
The flavonoids in dark chocolate also support the skin’s natural defense mechanisms and may even enhance the skin’s photoprotective capacity over time with regular consumption. Additionally, dark chocolate contains minerals like copper, iron, and magnesium that support various aspects of skin health and cellular repair.
To maximize benefits, choose high-quality dark chocolate with minimal added sugar and enjoy a small portion (about 20-30 grams) daily as part of a balanced diet. Remember that chocolate should complement—not replace—other protective measures like sunscreen and proper skincare.

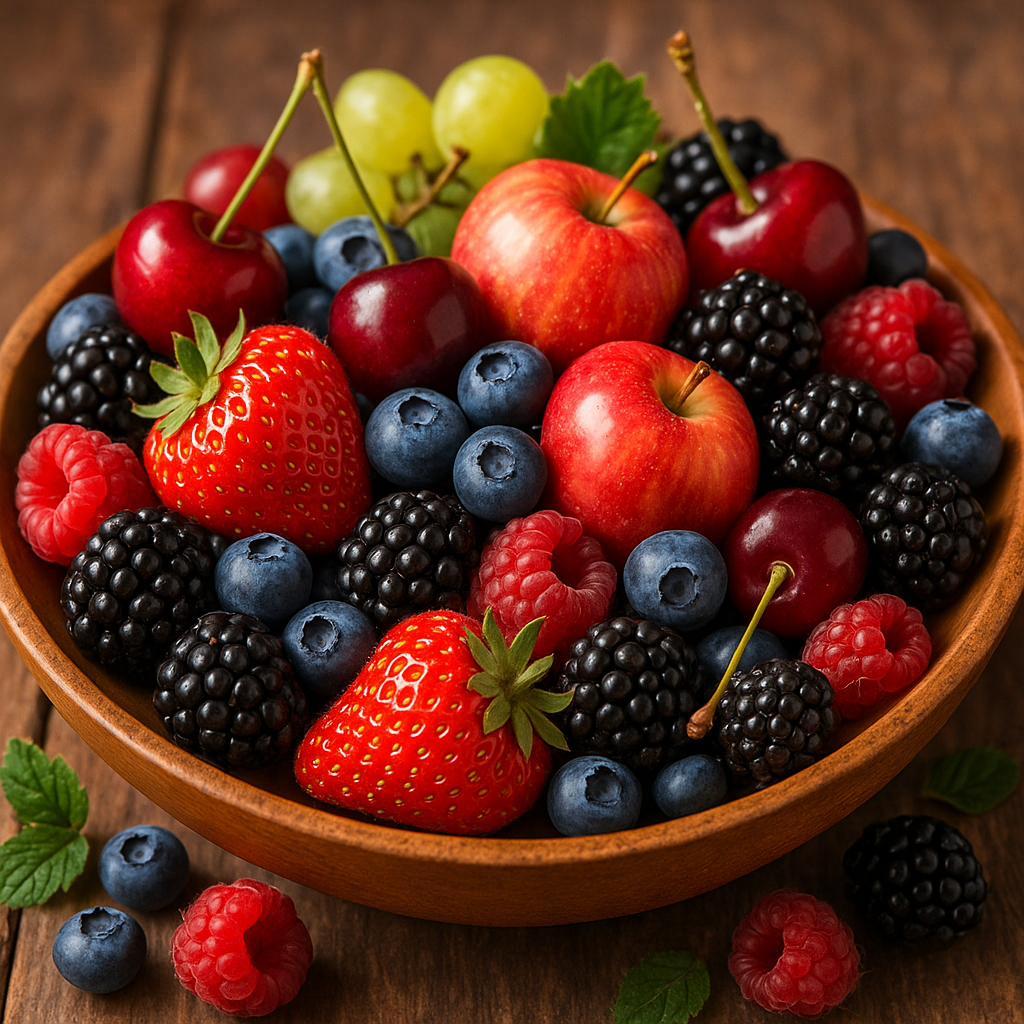
5. Eat Polyphenol-Rich Fruits
Polyphenols are naturally occurring compounds found abundantly in plant-based foods, and they represent one of your most powerful dietary tools for combating UV-related skin damage. These compounds function as antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, and have been shown in numerous studies to help protect against and repair UV-induced damage at the cellular level.
Different fruits contain varying types and concentrations of polyphenols, each offering unique protective benefits. Berries—including blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries—are exceptionally rich in anthocyanins, a type of polyphenol with strong antioxidant properties. Grapes, especially red and purple varieties, contain resveratrol, which has been extensively studied for its skin-protective effects.
Apples and pears provide quercetin, a flavonoid that helps reduce inflammation and supports the immune system. Cherries, particularly tart varieties, contain high levels of multiple polyphenol types and have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects that can help soothe post-tanning skin irritation from within.
Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, and lemons offer vitamin C alongside their polyphenol content, providing dual benefits for collagen synthesis and antioxidant protection. Pomegranates contain ellagic acid, which research suggests may help prevent collagen breakdown caused by UV exposure.
For optimal benefits, consume a variety of colorful fruits daily, aiming for at least 2-3 servings. Fresh whole fruits provide more complete nutritional benefits than juices, as they retain fiber and other compounds that work synergistically with polyphenols.

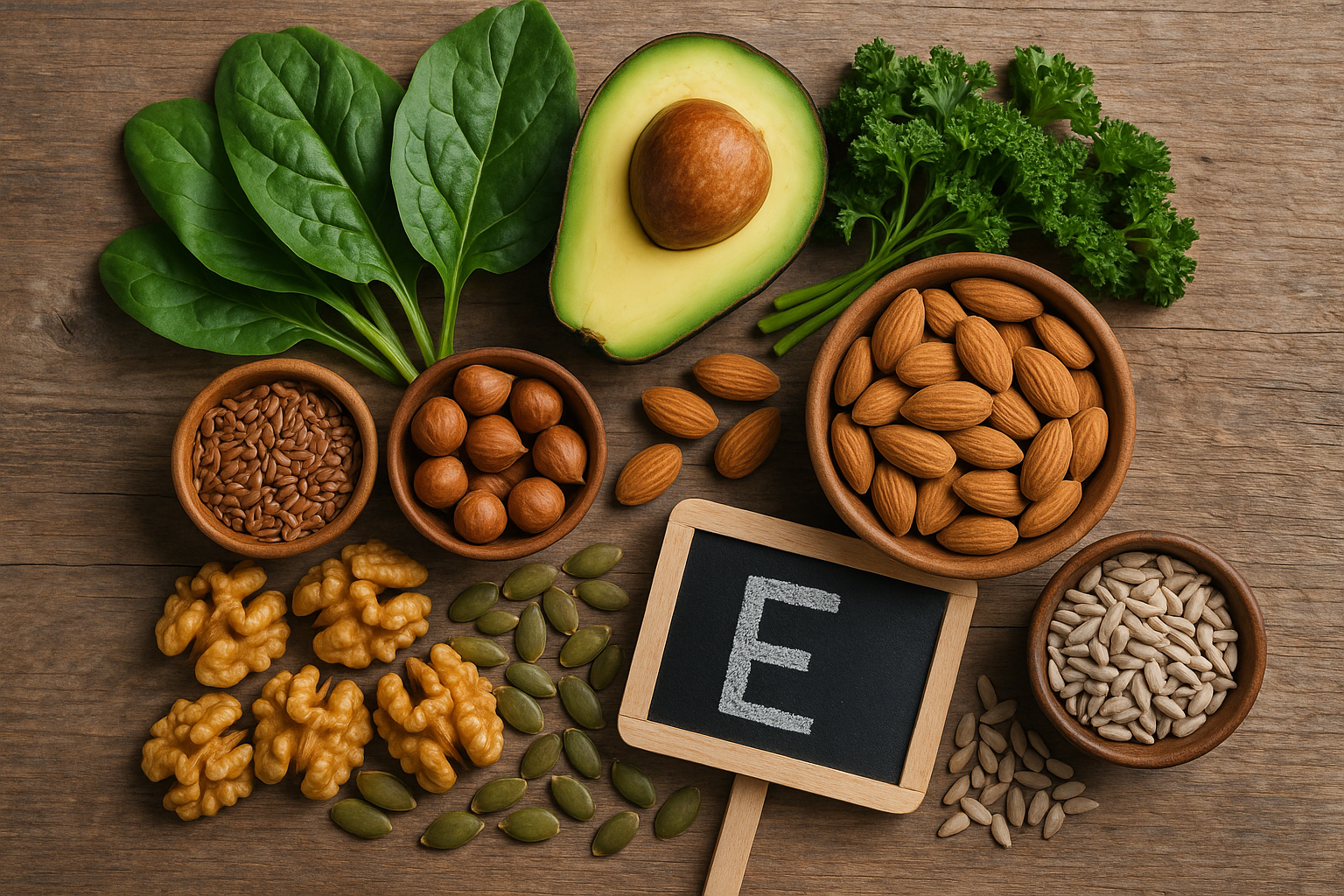
6. Supplement with Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that plays a critical role in protecting skin from oxidative stress caused by UV radiation. This essential nutrient exists in eight different forms, with alpha-tocopherol being the most biologically active and beneficial for skin health. Vitamin E works both topically and internally to neutralize free radicals, support the skin’s natural repair processes, and enhance the effectiveness of other antioxidants like vitamin C.
After tanning, your skin’s vitamin E stores are depleted as this nutrient is consumed in the process of neutralizing UV-generated free radicals. Replenishing these stores through diet and supplementation helps accelerate skin recovery, reduce inflammation, and minimize long-term damage. Research has shown that adequate vitamin E levels can help reduce erythema (skin redness), support the skin barrier function, and may even provide some degree of photoprotection when combined with other antioxidants.
Excellent dietary sources of vitamin E include nuts (particularly almonds, hazelnuts, and peanuts), seeds (sunflower seeds and pumpkin seeds), plant-based oils (wheat germ oil, sunflower oil, and olive oil), avocados, spinach, and fortified cereals. Consuming these foods with healthy fats enhances vitamin E absorption, as it is fat-soluble.
If you choose to supplement with vitamin E, consult with a healthcare provider about appropriate dosing, as excessive supplementation can have adverse effects. For most adults, 15mg (22.4 IU) daily is sufficient, though individual needs may vary based on factors like UV exposure levels and overall diet quality.

Additional Post-Tanning Care Considerations
Beyond these core strategies, several other practices can enhance your post-tanning skincare routine and help maintain optimal skin health. Avoid hot showers or baths immediately after tanning, as high temperatures can further dehydrate skin and increase inflammation. Instead, opt for lukewarm water and limit bathing time to prevent excessive moisture loss.
Wear loose, breathable clothing after tanning to avoid friction against sensitive skin and allow proper air circulation. Natural fabrics like cotton are ideal as they won’t trap heat or moisture against the skin.
Continue using broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, even after developing a tan. Melanin provides only minimal sun protection (equivalent to SPF 2-4), so you remain vulnerable to UV damage and should maintain consistent photoprotection practices.
Monitor your skin carefully for any unusual changes, including new moles, changes in existing moles, persistent redness, or areas that don’t heal properly. Regular skin examinations by a dermatologist are recommended for anyone who tans regularly or has significant sun exposure history.
Finally, consider gradually reducing tanning frequency or exploring safer alternatives like self-tanning products that provide color without UV exposure. These modern formulations have improved dramatically and can deliver natural-looking results without the associated health risks of UV-based tanning methods.

Conclusion: Protecting Your Skin While Enjoying Your Tan
Achieving a beautiful tan doesn’t have to come at the expense of your skin’s health and longevity. By understanding the biological processes involved in tanning and implementing comprehensive aftercare strategies, you can minimize damage, maintain your results longer, and support your skin’s natural resilience. Remember that proper hydration—both internal and external—forms the foundation of post-tanning care, while strategic exfoliation, antioxidant-rich nutrition, and ongoing sun protection complete a holistic approach to tanned skin maintenance.
Whether you prefer natural sunbathing, controlled indoor tanning, or sunless tanning alternatives, prioritizing skin health through evidence-based aftercare practices will help you enjoy your glow while preserving the vitality and appearance of your skin for years to come. Your skin is your body’s largest organ and deserves thoughtful care, especially when subjected to the stresses of UV exposure or chemical tanning processes.


